The Current Situation of Titanium Alloy Structures By Laser Welding
The Current Situation of Titanium Alloy Structures By Laser Welding
1. Characteristics and Application Of Titanium Alloy
As an excellent marine metal, titanium alloy is characterized by excellent properties such as strong corrosion resistance, low density, high specific strength, easy processing, and good impact resistance. Based on the excellent performance of titanium alloy, titanium alloy is widely used on ships, mainly steam turbine spindles, pumps, valves, heat exchangers and other accessories. At the same time, because titanium alloy is non-magnetic, it will not be magnetized in a strong magnetic field. Titanium alloy ships built with this characteristic, especially nuclear submarines, are not easy to be discovered by the opponent's magnetic finder. Titanium alloy is an important supporting material to ensure the performance and technical and tactical level of naval equipment. Titanium alloy for naval equipment is an inevitable choice for the strategy of a maritime power. Countries around the world have successively researched and developed special titanium alloy series. Although titanium alloys have many benefits, there will still be some welding problems such as cracks in joints, pores, and easy reactions with oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen at high temperatures. This is worth in-depth research.
2. Research Status of Titanium Alloy Laser Welding
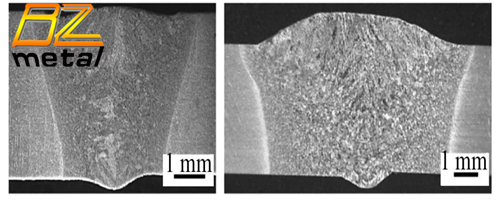
Laser welding technology is becoming more and more mature and is widely used in titanium alloy welding manufacturing. Ruifeng Li et al. used comparative tests of Ti-Al-Zr-Fe titanium alloys by laser welding and Laser-MIG composite welding to systematically analyze the effects of the differences in welding methods on the appearance, interface microstructure and mechanical properties of welded joints, which helps to better understand the effects of laser welding and laser MIG composite welding on the performance of Ti-Al-Zr-Fe titanium alloy joints. The study found that under the better process parameters, the welded joints do not have defects such as oxidation, cracks, pores, etc., and laser MIG composite welding can improve the formation of welds by filling the wire and increasing the heat input. Figure 6 shows the cross-sectional profile of laser welding and laser-MIG composite welding joints. In addition, bending tests have shown that the welded joints with laser-MIG composite welding have a higher bending angle and have better strength and ductility.
3. Cross-Sectional Profile of Laser Welding and Laser-MIG Composite Welding Joints
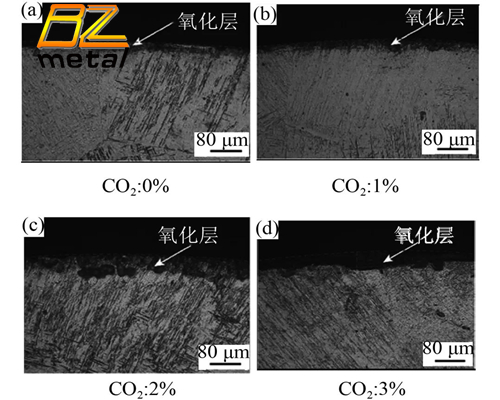
Jipeng Shi studied the influence of protective gases with different CO2 content on the forming of titanium alloy TA15 laser-TIG composite welding on the appearance of titanium alloy welds, and at the same time revealed the influence of CO2 on the oxidation of the bath surface, as shown in Figure 7. The test results show that the argon protective gas with a small amount of CO2 can significantly improve the formation of welds, and the CO2 concentration can be increased from 0% to 3%, which can inhibit the bite edge defects and stabilize the transition at the weld joints. The increase in CO2 content can increase the thickness of the oxide layer in the weld. The presence of the oxide layer can protect the bath from the protective gas and plasma arc, and keep the oxygen content in the weld stable. At the same time, it can prevent the bath from moving freely and change the formation of the bath. Wang Min and others conducted a comparative study of TIG welding and laser-arc composite welding of titanium alloy T-joints. The results show that the microstructure, weld forming and production efficiency of laser arc composite welding are better than that of TIG welding. In addition, the heat-affected zone of laser arc composite welding has a small tendency to grain growth, excellent fatigue performance and high joint strength. Cha Qiyou of Jiangnan Shipyard used Ti70 with a thickness of 4mm and TA5 with a thickness of 16 mm as the welding objects, and conducted preliminary process exploration of three high-energy density and high-efficiency titanium alloy welding methods: plasma arc welding (PAW), laser welding (LW) and laser-MIG (LW-MIG) composite welding. The test results show that the joints of laser welding and laser-MIG composite welding are of good quality. Due to its high degree of automation and welding efficiency, it has prospects for large-scale application in the field of shipbuilding.In addition, we tried to use the deep melting effect of high-power laser welding, and successfully welded the nail-shaped structure of the 4 mm Ti70 board + 16 mm TA5 board, which expanded the design scope for future ship designs.