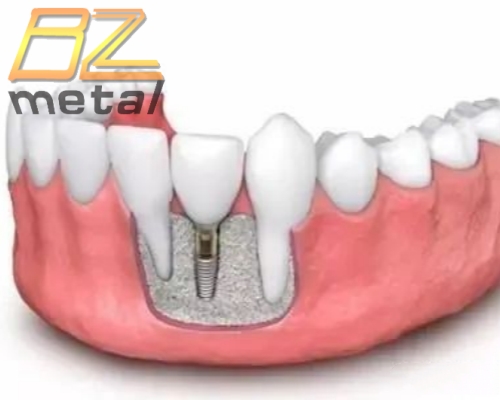
Titanium and Titanium Alloy Materials in Oral Implant Applications
Titanium and Titanium Alloy Materials in Oral Implant Applications
1. Pure Titanium
Since Branemark proposed the osseointegration theory, pure titanium and titanium alloys (mainly Ti-6Al-4V) have always been the materials of choice for oral implants. Studies have found that pure titanium has good biocompatibility and corrosion resistance, as well as excellent mechanical properties, including hardness, tensile strength, yield strength and fatigue strength. It can meet the needs of oral implants to perform functions. It has been widely used as an implant material in clinical practice and has achieved good repair results.
However, the gray color of titanium can pass through the thinner mucous membrane at the implant, which in turn affects the aesthetic effect of patients with thin gingival type. The elastic modulus of titanium is higher than that of human bone, the elastic modulus of titanium is 110 GPa, and the elastic modulus of human bone is 110 GPa.
The elastic modulus is 20~30 GPa, which will cause bone resortionment due to stressshields. With the increase of clinical applications, studies in recent years have found that pure titanium implants are at risk of peri-implant inflammation, and can release titanium ions to participate in gingivitis and periodontal inflammation.
In addition, titanium may be immunogenic and, as an allergen, cause type IV hypersensitivity reactions to metal implants in some patients with allergies. Therefore, scholars at home and abroad have been committed to researching and exploring oral implant materials that have better performance in all aspects and can replace pure titanium.
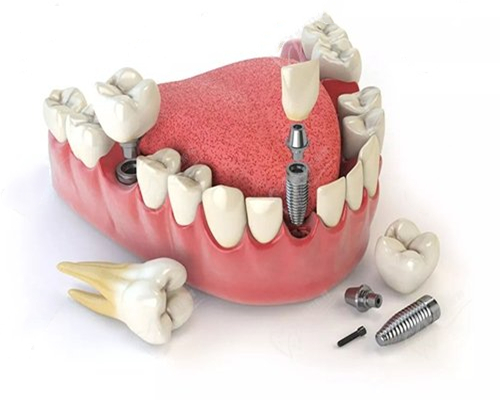
2. Titanium Alloy
Following the widespread application of pure titanium implants in clinical practice, titanium alloy oral implant materials have gradually developed. Compared with pure titanium, adding alloying elements can improve the corrosion resistance and processability of the material, and reduce the elastic modulus. Especially for narrow-diameter implants, it can also reduce the risk of fracture. The titanium alloy with more clinical applications is Ti-6Al-4V alloy. In recent years, relevant studies have found that Ti-6Al-4V alloy will release very small amounts of vanadium and aluminum ions. These two ions can cause harm to the human body, such as Alzheimer's disease, peripheral neuropathy, and osteoarthritis. Therefore, scholars began to focus their research on the development of non-toxic titanium alloys. Β-titanium alloying elements such as Nb, Zr, Ga, Mo, Pd, Se, Sn, Ta, Ge, etc. are considered safe and non-toxic alloying elements. Therefore, in the process of seeking a more ideal implant material, the alloying of titanium has become one of the hot topics in this field.
2.1 Titanium Zirconium Alloy(Ti-Zr)
Zirconium and titanium belong to the same main family, and the two have similar physical and chemical properties: they both have excellent corrosion resistance, ultra-high mechanical strength, excellent plasticity, etc., and have non-toxic effects on body tissues.
2.2 Titanium Niobium Alloy(Ti-Nb)
Titanium niobium alloy has gradually attracted the attention of scholars because of its good corrosion resistance and biocompatibility. Studies have shown that titanium-niobium alloy has sufficient corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, can promote osteogenesis, and has the potential to become an implant material, but its mechanical properties have yet to be confirmed by scholars.
2.3 Titanium Aluminum Niobium Alloy
Scholars are worried that Ti-6Al-4V alloy will release toxic vanadium ions and cause adverse reactions to the human body, so Ti-6Al-7Nb alloy was developed. Ti-6Al-7Nb alloy is non-toxic. It not only has similar mechanical properties to Ti-6Al-4V alloy, but also has strong corrosion resistance. In recent years, it has gradually entered the eyes of oral implant scholars.
Studies have shown that Ti-6Al-7Nb alloy not only retains the good mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy, but also has better biocompatibility, biosafety and corrosion resistance. It is more conducive to the adhesion and proliferation of osteoblasts, and its bone binding ability is comparable to that of pure titanium.
2.4 Titanium Niobium Tin Alloy(Ti-Nb-Sn)
The elastic modulus of titanium niobium tin alloy is about 40 GPa, it is non-cytotoxic, has good corrosion resistance and bone tissue compatibility. Titanium niobium tin alloy has biological potential and bone binding energy comparable to pure titanium
force.
2.5 Titanium Tantalum Zirconium Alloy (Ti-Ta-Zr)
After the synthesis of titanium, tantalum and zirconium alloys, tantalum can reduce the elastic modulus of the material, and zirconium can improve its corrosion resistance. Compared with pure titanium, titanium-tantalum-zirconium alloy has a low elastic modulus, better corrosion resistance and hydrophilicity, and better bone binding ability, which is expected to become an alternative to pure titanium implant material.
2.6 Titanium Niobium Zirconium Alloy (Ti-Nb-Zr)
Titanium, niobium and zirconium alloy has great ductility, an elastic modulus of 79 GPa, excellent plastic deformation ability, and good mechanical properties and biocompatibility. Titanium niobium zirconium alloy has excellent mechanical properties, biocompatibility and corrosion resistance, and has the potential to become a candidate material for oral implants.
2.7 Titanium Niobium Zirconium Tin Alloy (Ti-Nb-Zr-Sn)
Titanium niobium zirconium tin alloy is a new type of titanium alloy with high strength and low elastic modulus. Nune et al. believe that Ti-24nb-4Zr-8SN alloy is conducive to the adhesion, proliferation, differentiation, mineralization and synthesis of related proteins of osteoblasts due to its unique chemical properties and high hydrophilic properties. It is expected to be used in clinical practice in the future.
2.8 Titanium Niobium Tantalum Zirconium Alloy(Ti-Nb-Ta-Zr)
Titanium niobium zirconium tantalum alloy has similar histocompatibility to Ti-6Al-4V alloy, which can promote the proliferation of osteoblasts and improve the activity of alkaline phosphatase. Therefore, titanium niobium tantalum zirconium alloy has the potential to become an alternative material for pure titanium implants.
2.9 Titanium Niobium Zirconium Tantalum Silicon Alloy(Ti-Nb-Zr-Ta-Si)
In recent years, oral implant scholars have gradually developed and researched a new five-phase titanium alloy-titanium niobium zirconium tantalum silicon alloy. The experimental results show that the bone binding capacity of titanium niobium zirconium tantalum silicon alloy implants is comparable to that of pure titanium, which can improve the mineralization and deposition rate of surrounding bone in the early stage after implant implantation. However, scholars have only done preliminary research, and the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of the material still need in-depth research and confirmation.